
If so, you can reject the null hypothesis and conclude that the two groups are in fact different. You can compare your calculated t-value against the values in a critical value chart to determine whether your t-value is greater than what would be expected by chance. In this formula, t is the t-value, x 1 and x 2 are the means of the two groups being compared, s 2 is the pooled standard error of the two groups, and n 1 and n 2 are the number of observations in each of the groups.Ī larger t-value shows that the difference between group means is greater than the pooled standard error, indicating a more significant difference between the groups. The formula for the two-sample t-test (a.k.a. You can calculate it manually using a formula, or use statistical analysis software. The t-test estimates the true difference between two group means using the ratio of the difference in group means over the pooled standard error of both groups.

comparing the acidity of a liquid to a neutral pH of 7), perform a one-sample t-test. If there is one group being compared against a standard value (e.g.two different species, or people from two separate cities), perform a two-sample t-test (a.k.a. If the groups come from two different populations (e.g.measuring before and after an experimental treatment), perform a paired t-test. If the groups come from a single population (e.g.One-sample, two-sample, or paired t-test? When choosing a t-test, you will need to consider two things: whether the groups being compared come from a single population or two different populations, and whether you want to test the difference in a specific direction.
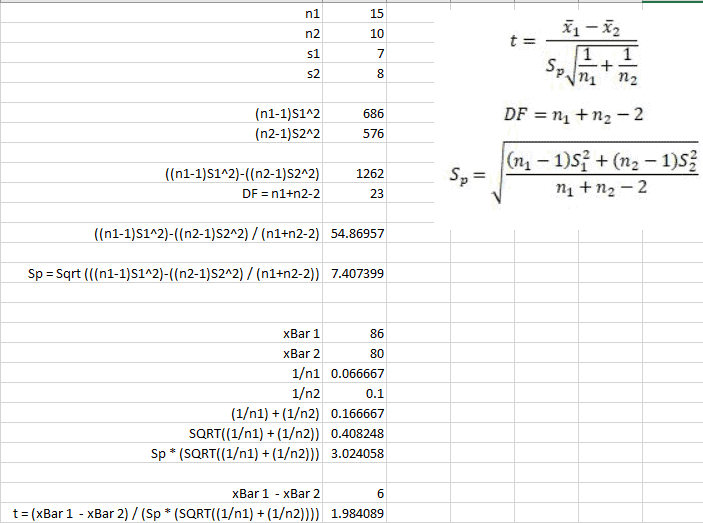
If your data do not fit these assumptions, you can try a nonparametric alternative to the t-test, such as the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank test for data with unequal variances.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
